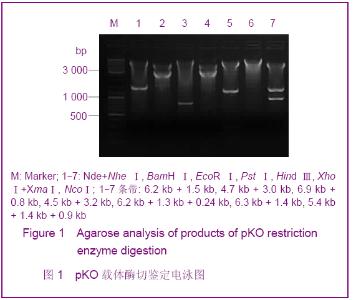
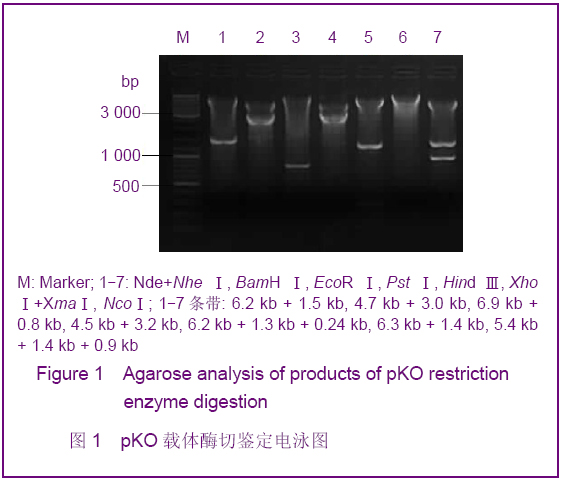
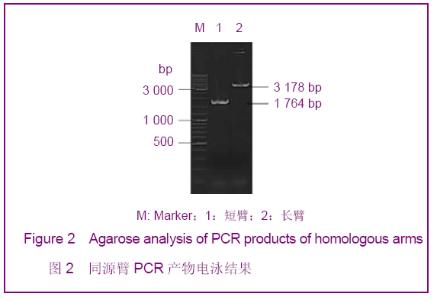
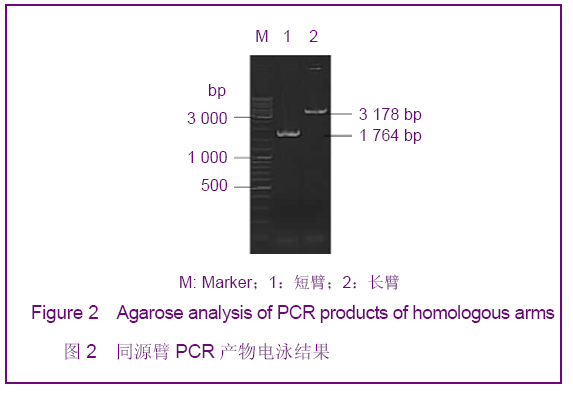
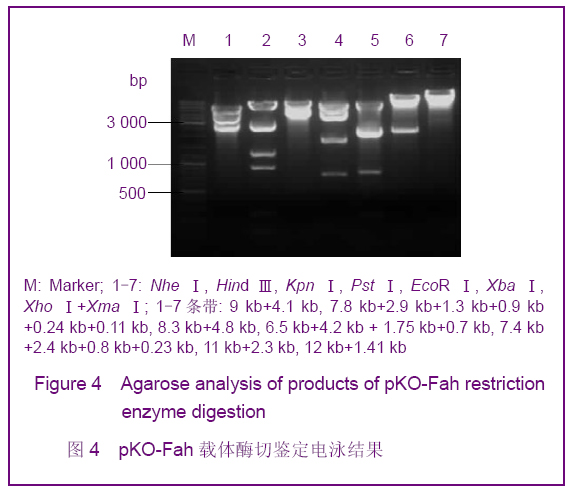
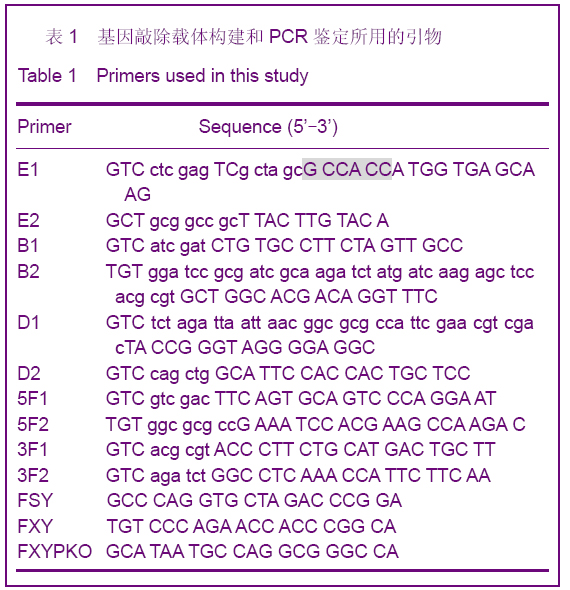
| [1] Smithies O, Gregg RG, Boggs SS, et al. nsertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985;317(6034):230-234.[2] Dou W.Guowai Yixue:Yichuanxue Fence.2005; 28(4):193-195.窦薇.基因打靶技术及其发展和应用[J].国外医学:遗传学分册,2005,28(4):193-195.[3] Thompson S, Clarke AR, Pow AM, et al. Germ line transmission and expression of a corrected HPRT gene produced by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1989;56(2):313-321.[4] Koller BH, Hagemann LJ, Doetschman T, et al. Germ-line transmission of a planned alteration made in a hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(22):8927-8931.[5] Buehr M, Meek S, Blair K, et al. Capture of authentic embryonic stem cells from rat blastocysts. Cell. 2008;135(7): 1287-1298. [6] Li P, Tong C, Mehrian-Shai R, et al. Germline competent embryonic stem cells derived from rat blastocysts. Cell. 2008; 135(7):1299-1310.[7] Ying QL, Wray J, Nichols J, et al. The ground state of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nature. 2008;453(7194): 519-523.[8] Tong C, Li P, Wu NL, et al. Production of p53 gene knockout rats by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2010;467(7312):211-213.[9] Smits BM, Gould MN. “Gene targeting in the rat? Cut it out!”. Mol Interv. 2009;9(5):226-229.[10] Manis JP. Knock out, knock in, knock down--genetically manipulated mice and the Nobel Prize. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357(24):2426-2429.[11] Aitman TJ, Critser JK, Cuppen E, et al. Progress and prospects in rat genetics: a community view. Nature Genetics. 2008;40(5):516-522.[12] Grompe M, al-Dhalimy M, Finegold M, et al. Loss of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase is responsible for the neonatal hepatic dysfunction phenotype of lethal albino mice. Genes Dev. 1993;7(12A):2298-2307.[13] Wang X, Lagasse E, Grompe M, et al. Liver repopulation and correction of metabolic liver disease by transplanted adult mouse pancreatic cells. Am J Pathol. 2001;158(2):571-579.[14] Wang X, Foster M, Al-Dhalimy M, et al. The origin and liver repopulating capacity of murine oval cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100 Suppl 1:11881-11888.[15] Wilber A, Wangensteen KJ, Wang X, et al. Messenger RNA as a source of transposase for sleeping beauty transposon-mediated correction of hereditary tyrosinemia type I. Mol Ther. 2007;15(7):1280-1287.[16] Wangensteen KJ, Wilber A, Wang X, et al. A facile method for somatic, lifelong manipulation of multiple genes in the mouse liver. Hepatology. 2008;47(5):1714-1724.[17] Hamra FK. Gene targeting: Enter the rat. Nature. 2010;467 (7312): 161-163.[18] Wang H.Zhongguo Xiandai Yiyao Zazhi.2009; 11(3):131-134.王会.基因打靶技术研究及其应用[J].中国现代医药杂志,2009, 11(3):131-134.[19] Wang X, Montini E, Grompe M, et al. Kinetics of liver repopulation after bone marrow transplantation. Am J Pathol. 2002;161(2):565-574.[20] Azuma H, Paulk N, Grompe M, et al. Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah-/-Rag2-/-IL2rg-/- mice. Nature Biotechnology. 2007;25(8):903-910.[21] Su BL,Wang X.Zhongguo Yaoke Daxue Xuebao.2009; 40(6): 553-558.苏宝亮,王欣. Fah基因剔除小鼠在肝细胞移植中的应用及其病理学变化[J].中国药科大学学报,2009,40(6):553-558.[22] Su BL,Hu YP. Zhongguo Kexue: Shengming Kexue.2010;40 (10): 929-937.苏宝亮,胡以平.人成体肝细胞在Fah-/-Nod/Scid小鼠肝脏中的显著增殖[J].中国科学:生命科学,2010,40(10):929-937.[23] Tesson L, Cozzi J, Ménoret S, et al. Transgenic modifications of the rat genome. Transgenic Res. 2005;14(5):531-546. |